Planning Poker Via Skype
Planning Poker (also known as Scrum Poker) is a very popular technique proposed in 2002 by James Grenning. Each player uses a set of cards with Fibonacci sequence numbers on it to estimate the overall effort of a task in Story Points.
Using Skype Meeting Broadcast to host a live event will lessen the stress of the preparation, since with only a few clicks and a strong internet connection, you’re already good to go. Wider reach With up to 10,000 attendees for an event, you can have a wide audience reach from across the globe. Then, set up a private game and invite your friends to play using the Club ID Number and the invitation code. You can play various Poker Games on PokerStars, like Texas Hold'em, Omaha, Stud, and Razz. Planning poker is a team game for estimating work. It's often used by Scrum teams during backlog refinement workshops or sprint planning to estimate the size of product backlog items. In my Dynamics 365 projects, we play planning poker to estimate the complexity of our epics, user stories, chores, bugs and spikes.
Planning Poker procedure
Planning Poker Via Skype Chat
Take in mind that with great popularity came multiple variations of this technique, each team tend to adapt it for their needs. Classic procedure is as follows:
Planning Poker Via Skype Download
- The Product Owner provides a short overview of a user story that will be estimated by the team. The team can ask questions. Potential clarifications can influence the initial scope.
- Everyone from the team picks one card from his set (1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13 …) and lays it face down in front of him.
- When everyone is ready, the team is turning over cards.
- Members with the highest and lowest estimates should justify their votes and discussion continues.
- Repeat steps 2-4 until a consensus is reached.
Mind the fact, that consensus doesn’t necessarily mean that everyone needs to put the same number. The team might just agree to disagree and put the average or largest number as an estimate.
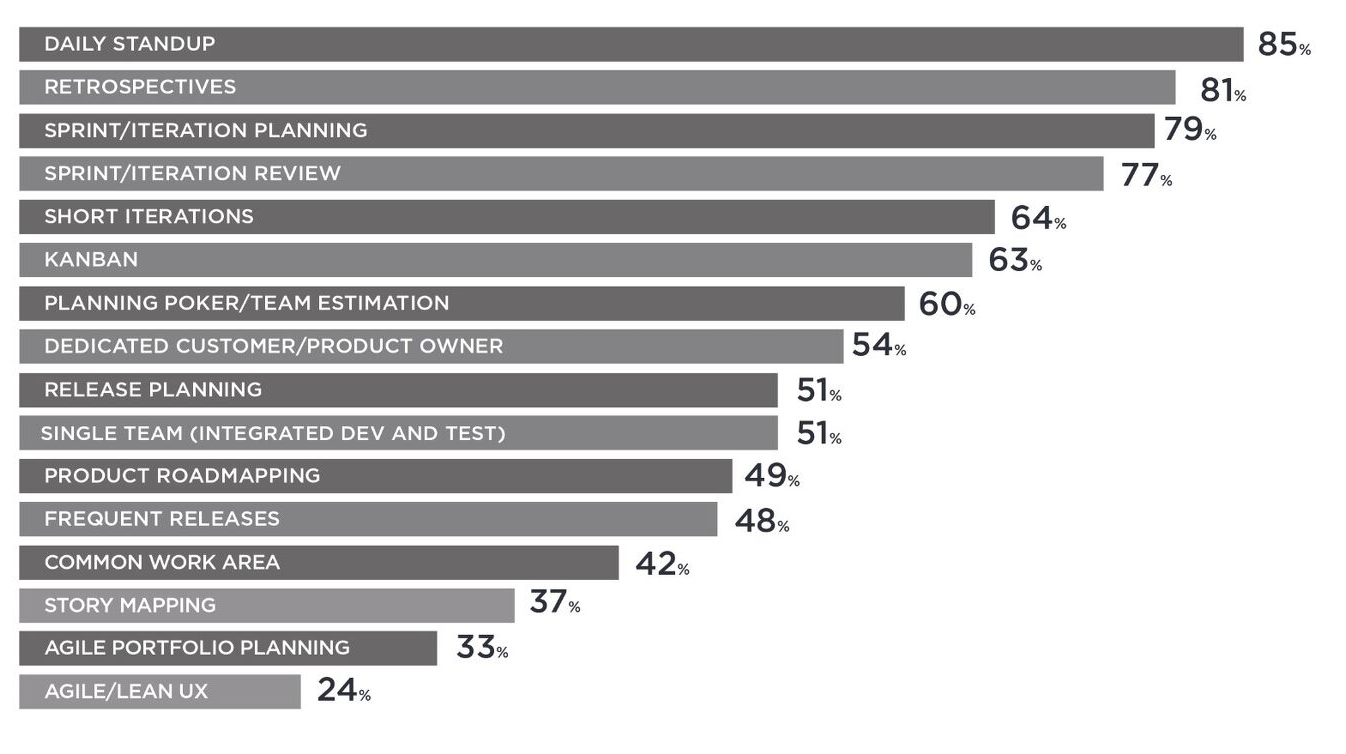
When to use Planning Poker?

With a strong focus on the discussion, this approach helps to spread the common knowledge of user stories across the team. So Planning Poker is ideal for Scrum Teams, preferably when it is unknown which developer will deal with the issue.
This method shows high accuracy in estimations.
What are the disadvantages?
Although Planning Poker deals well with new features it throttles when it comes to unknown or uncertain things such as research or bugs.
Another important factor is that this is rather time-consuming. From my experience estimating one task often takes more than 15 minutes and the bigger team the longer it takes to find the consensus.
Planning Poker (also known as Scrum Poker) is a very popular technique proposed in 2002 by James Grenning. Each player uses a set of cards with Fibonacci sequence numbers on it to estimate the overall effort of a task in Story Points.
Planning Poker procedure
Take in mind that with great popularity came multiple variations of this technique, each team tend to adapt it for their needs. Classic procedure is as follows:

- The Product Owner provides a short overview of a user story that will be estimated by the team. The team can ask questions. Potential clarifications can influence the initial scope.
- Everyone from the team picks one card from his set (1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13 …) and lays it face down in front of him.
- When everyone is ready, the team is turning over cards.
- Members with the highest and lowest estimates should justify their votes and discussion continues.
- Repeat steps 2-4 until a consensus is reached.
Mind the fact, that consensus doesn’t necessarily mean that everyone needs to put the same number. The team might just agree to disagree and put the average or largest number as an estimate.
When to use Planning Poker?
With a strong focus on the discussion, this approach helps to spread the common knowledge of user stories across the team. So Planning Poker is ideal for Scrum Teams, preferably when it is unknown which developer will deal with the issue.

This method shows high accuracy in estimations.
What are the disadvantages?
Although Planning Poker deals well with new features it throttles when it comes to unknown or uncertain things such as research or bugs.
Another important factor is that this is rather time-consuming. From my experience estimating one task often takes more than 15 minutes and the bigger team the longer it takes to find the consensus.